2025. 4. 29. 22:00ㆍCS/CCNA
OSPF (part 1)
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
-> Routers independently use map calculated as the best routes
-> Dijkstra's algorithm (다익스트라 알고리즘)
-> v1 : old / v2: IPv4 (common used) / v3: IPv6
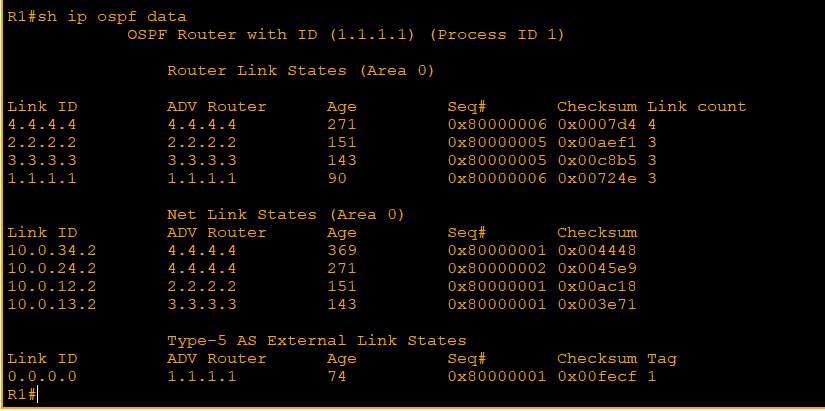
-> Store info about NW in LSAs (Link State Advertisements) organized in structure LSDB (Link State database)
-> Router flood LSAs until develop the same map of NW(LSDB)
LSA flooding :
-> tell its negibors about new NW
-> flood sharing the same LSDB
Areas (divide up NW):
-> small NW be single-area
-> larger NW be single-area would be negetive effect
<prob>
- SPF takes more time to cal / processing power
- larger LSDB needs more mem
- small change occurs every router's flooding it
<sol>
- divide into smaller area
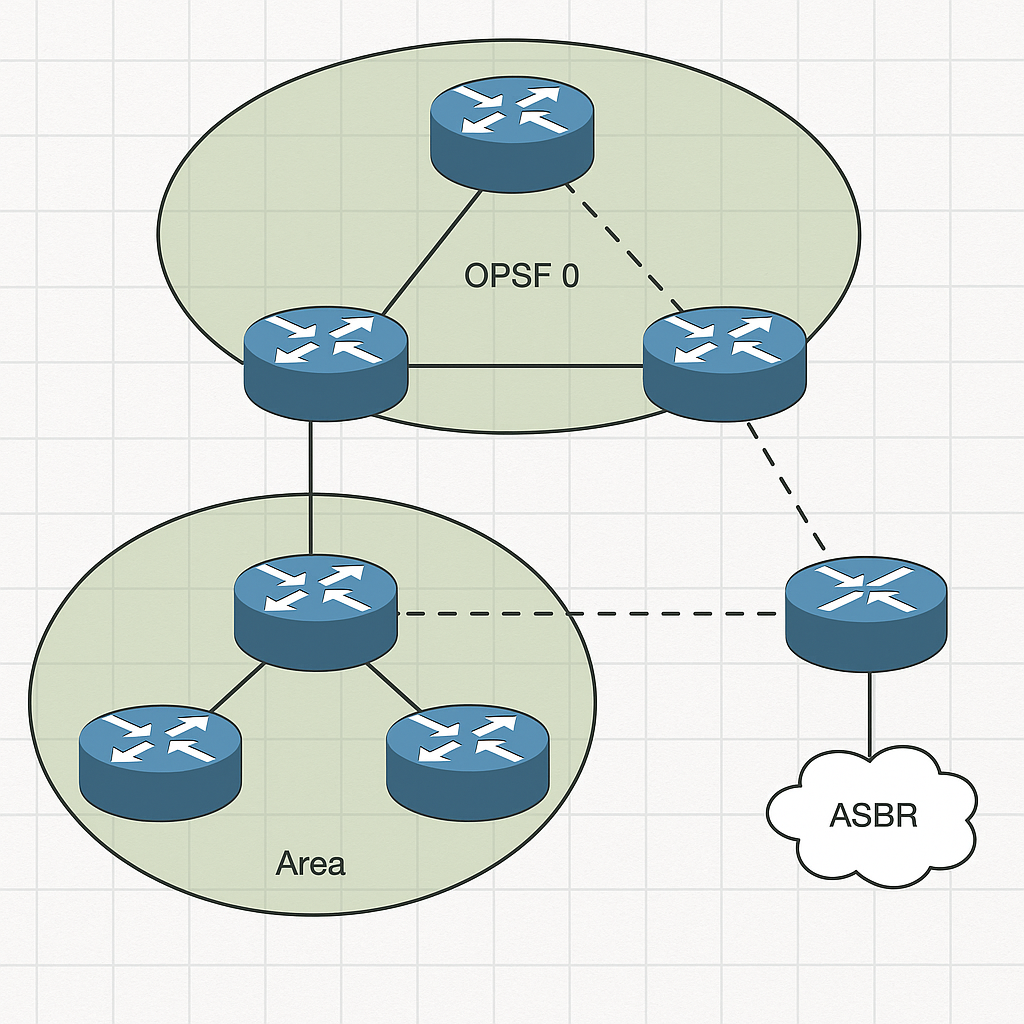
Terms
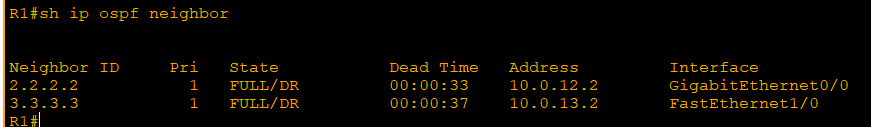
1. Area: share same LSDB
2. backbone area: must connect to all area
3. internal routers: routers inside the area
4. ABRs(Area border routers): covered multi areas
5. backbone router: all routers in the backbone area
6. intra-area route: transmission in the same area
7. interarea route: transmission out of the area
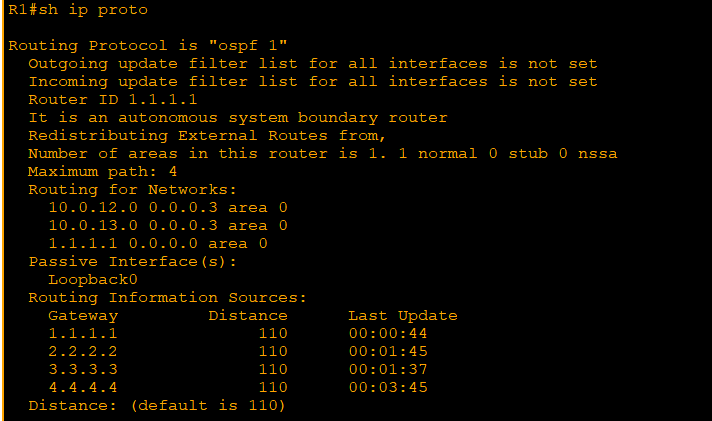
8. Autonomous system boundary router (ASBR): connect to the internet
(config) router ospf 1[process ID]
* process ID (!= RIP, should match ID in the same RIP)
logically significant (diff ID can become ISPF neigbor)
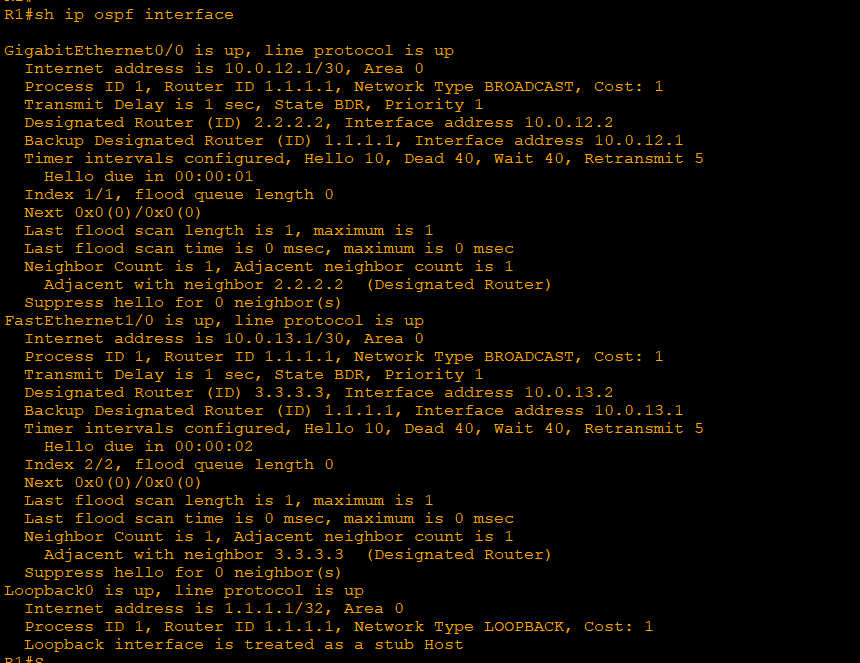
Router ID priority (same as EIGRP)
1) manual
2) loopback int
3) physical int
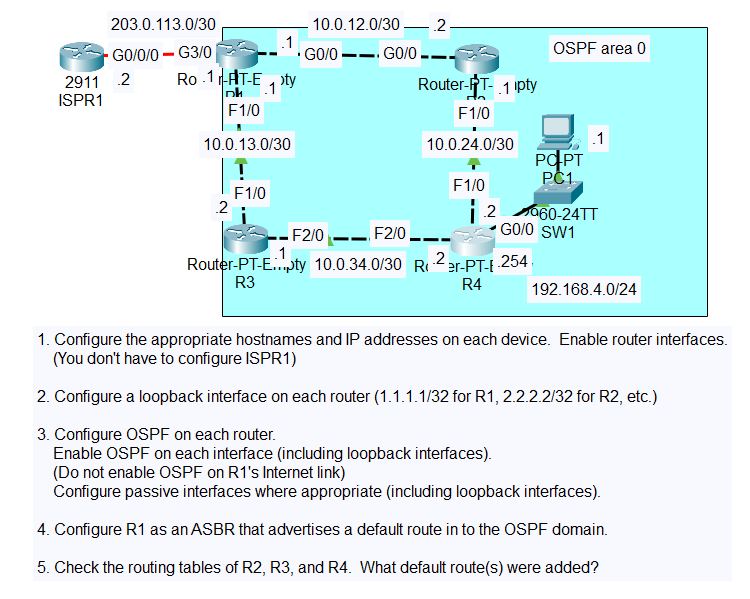
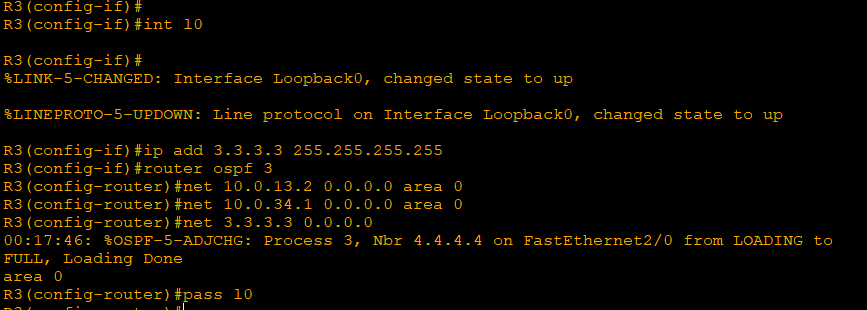
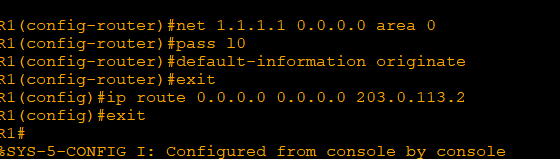
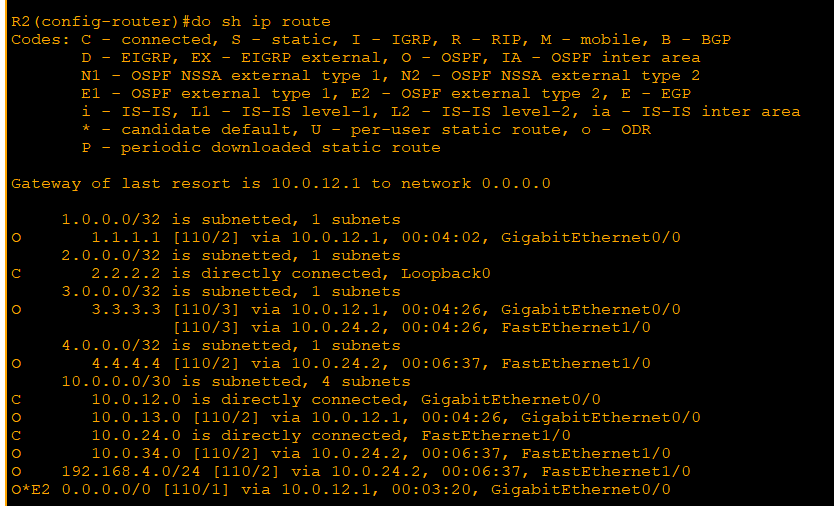
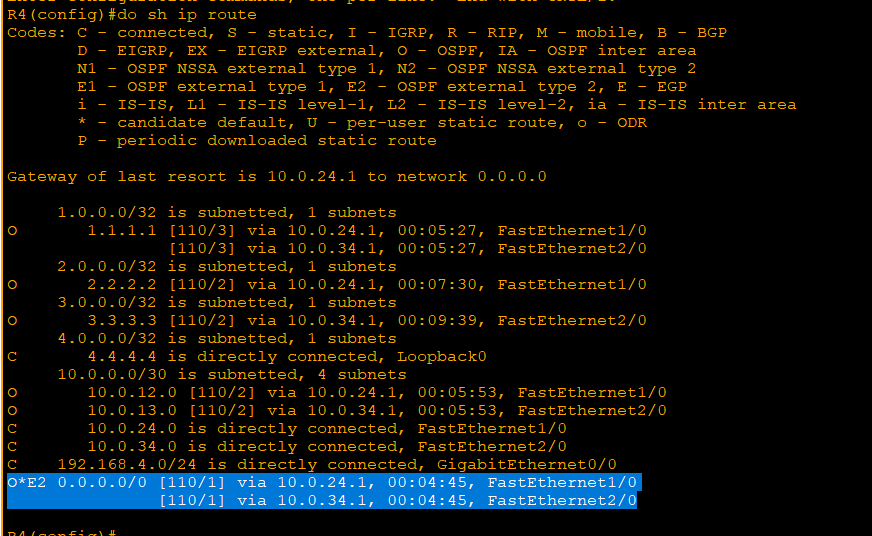
'CS > CCNA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day 28: OSPF (part 3) (0) | 2025.05.02 |
|---|---|
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day 27: OSPF (part 2) (1) | 2025.04.29 |
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day 25: RIP & EIGRP (0) | 2025.04.27 |
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day 24: Dynamic Routing (0) | 2025.04.26 |
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day 23: Ethernet Channel (1) | 2025.04.25 |