2025. 3. 22. 21:04ㆍCS/CCNA
★ Routing Fundamentals, Static Route
Switch: Mac address table
Router: Routing table
- Connected and Local routes
- Static Routing
Routing is the process routers use to determine the path that IP packets should take over a NW to reach their destin.
-> Routers store routes to all of their known destin in a routing table
-> when routers receive packets, look in routing table
- Dynamic routing: Daynamic routing protocols (OSPF) automatically bulid their routing tables
- Static routing: manually congifures routes on the router
- route tells the routher to send to destin X, you should sen the pakcet to next-hop(next router in the path to the destin)
-> or if directly connected to the router(Connected route), send directly to destin
-> or if it is own IP(Local route), receive packet for yourself
WAN: Wide Area Network
-> a nw that extends over a large geographical area
//CLI
Routing Table
R1# show ip route
-> Codes legend(범례) in the output of show ip route lists which routers can use
-> L - Local route: actual IP adrs configured on the interface(with /32 netmask)
## if IP is 192.168.1.1/24, route will be to 192.168.1.0/24
-> C - Connected route: route to the NW the interface is connected to (with actual netmask configured on inter)
## if IP is 192.168.1.1/24, route will be to 192.168.1.0/32
-> When configure IP adrs with no shutdown, routes will automatically be added to routing table(L C)
-> A route matched a destination if the packet's destin IP adrs is part of the NW specified in the route.
-> If packet doensn't have a match the packet's destin, router will drop the packet. (!= switch, flood frames)
-> Use the most specific matching route to forward the packet. (!= switch, exact same MAC)
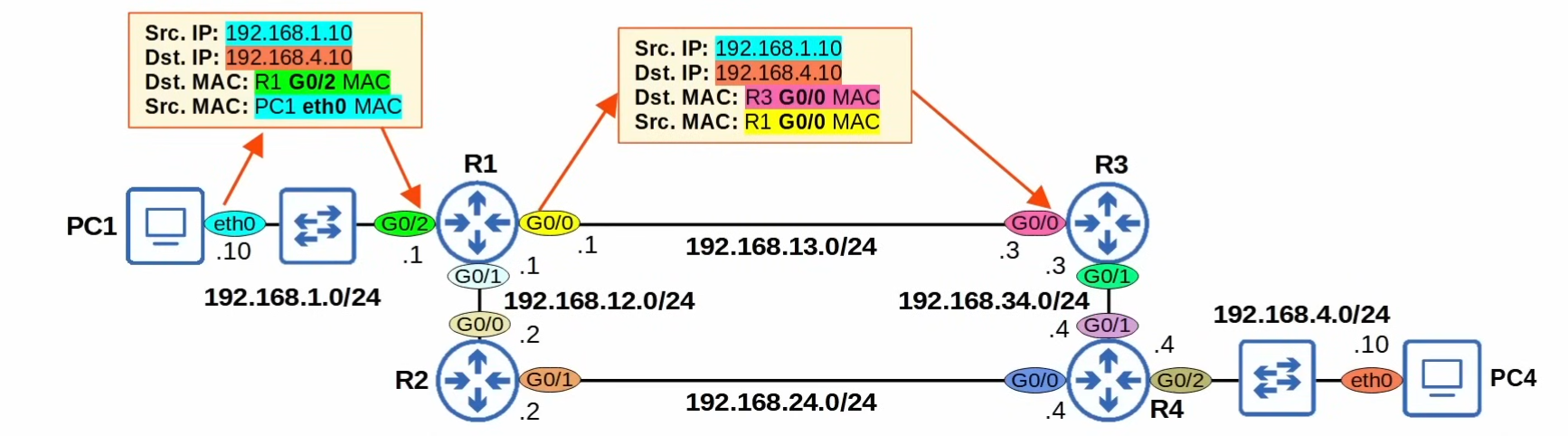
Static Route configuration:
-> Two-way reachability (PC1 can send packets to PC4, and opposite is possible)
-> manually configured (using Static routes)
-> To allow PC1 and PC4 to communicate with over the NW, configure Static routes on R1, R3, and R4
(if we consider only R1- R3 - R4 route)
//CLI
R1(config)# ip route destin-ip-address netmask next-hop
## R1(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.13.3
## >> S 192.168.4.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.13.3
* [1/0] = [Administrative Distance/Metric]
R2(config)# ip route ip-adrs netmask exit-interface
## R2(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 g0/0
## >> Direcly conntected
R2(config)# ip route ip-adrs netmask exit-interface next-hop
## R2(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 g0/0 192.168.24.4
## >> S 192.168.4.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.24.4
-> Static routes having only exit-interface rely on a feature called Proxy ARP to function
-> Neither is 'better' than other
Default route(default gatway):
-> 0.0.0.0/0 (least specific route; includes every destin IP)
-> If router doesn't have any more specifics, the router will forward the packet using default route
-> Used to direct traffic to the Internet
* More specific routes are used for destin in internal corporate network(Router)
* Traffic to destins outside of the internal NW is sent to the Internet
##>> * - candiate default
Q1. IP address configured on a router interface will appeare in the routing table as what kinds of route?
>Local
Q2. congifure a default route on a Cisco router?
> R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.255 (cannot specify prefix length with '/')
Acronym:
- WAN: Wide Area Network
'CS > CCNA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day13: Subnetting(Part1) (0) | 2025.03.24 |
|---|---|
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day12: Life of a Packet (0) | 2025.03.23 |
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day10: IPv4 Header (1) | 2025.03.21 |
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day9: Switch Interfaces (0) | 2025.03.20 |
| <Jeremy's IT Lab> Day8: IPv4 Addressing(Part2) (1) | 2025.03.19 |